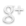Forty years ago today — April 5, 1973 — an Atlas Centaur rocket launched from Cape Canaveral carrying the Pioneer 11 space probe.

(Pioneer 11. NASA image.)
Pioneer 11 launched at 02:11 April 6th UTC, though it was still April 5th in Florida when it lifted off. It followed its sister ship, Pioneer 10, which had launched a little over a year before (on March 2, 1972).
Pioneer 11 was the first spacecraft to travel to Saturn, and returned close-up pictures of the ringed planet. On its way to Saturn, it used Jupiter’s gravity for course correction, and in so doing became the first spacecraft to photograph Jupiter’s polar region.
Pioneer 11 passed by Saturn on September 1, 1979, and then continued on toward the edge of the Solar System and the constellation Sagittarius. Contact with the spacecraft was lost in late 1995.