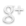Today the LCROSS (Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite) is supposed to launch on an Atlas-V rocket, along with the LRO (Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter). LCROSS is specifically designed to check for water in shadowed craters at the lunar south pole.

(Artist’s conception of LCROSS approach to the moon, from http://lcross.arc.nasa.gov/. Click to enlarge.)
The mission profile involves crashing the Centaur upper stage into an as-yet-undetermined crater, with the LCROSS vehicle and its sensors following close behind. Not only will LCROSS itself examine the ejecta for signs of water, but the debris from the impact is expected to rise high enough above the moon’s surface to be visible to earth-based instruments as well. Analysis should show whether hydrogen detected by previous missions (e.g., Clementine) is in the form of water.
Why does this demonstrate the hazards of writing near-future SF? Because I know of a novel — written by me, for which I’m trying to find a publisher and an agent — in which a major part of the plot is a difficult journey to the lunar south pole to retrieve ice to keep the fledgling colony alive.
The LCROSS mission could either lend credence to my treatment of lunar conditions, or it could make the novel much more fiction than science. So here’s what I would like:
- First, I’d like the mission to detect appreciable amounts of water ice, no matter what crater they choose.
- Second, I’d like NASA to select a different crater than I did, so no matter what LCROSS finds my story could still be plausible. I picked Faustini Crater for my ice expedition, so anywhere else, okay?
Such is the hazard of writing realistic, near-future SF — your assumptions may be subject to verification before your story ever sees print! (Here I repeat my hope that my story will indeed see print. Time will tell. But if you know of a publisher looking for such a story, point them my way!)
If you want more info, here’s the NASA page about the mission.
[BREAK, BREAK]
And, how about a little space history: Five years ago today — June 18, 2004 — marked the first time a U.S. astronaut was in space when his child was born on Earth. Edward Michael “Mike” Fincke was aboard the International Space Station when his wife gave birth to their second child.