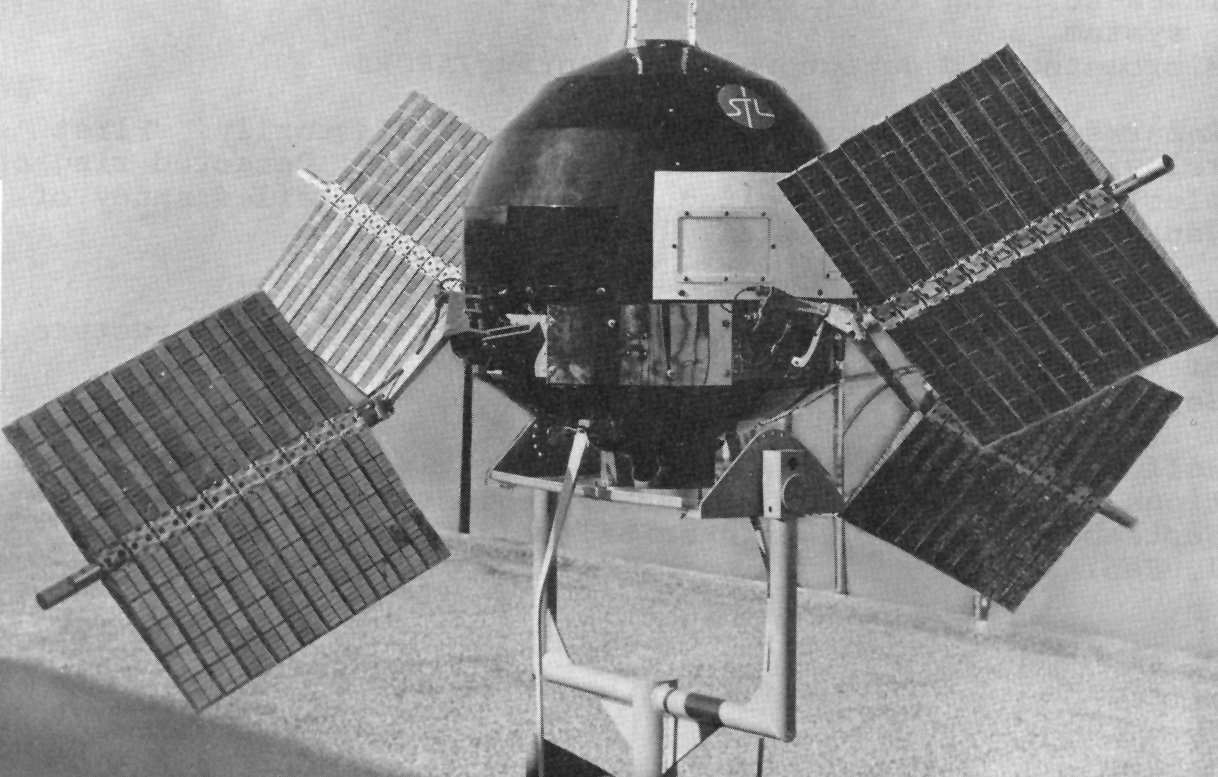
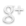Forty-five years ago today — August 19, 1964 — a Thor Delta rocket launched the Syncom-3 satellite out of Cape Canaveral.
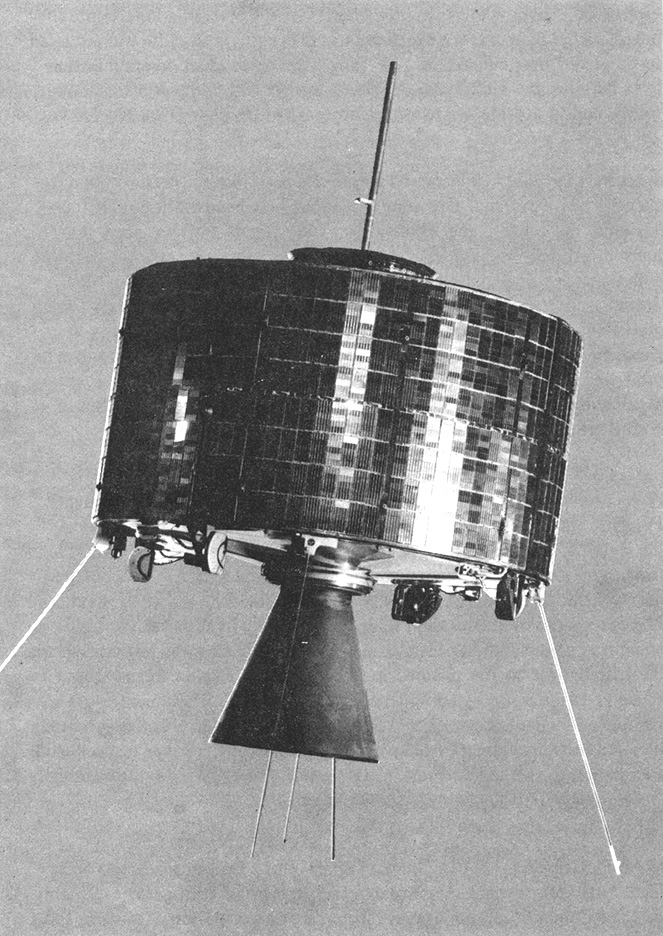
(Syncom-3 satellite. Image from NASA’s Space Science Data Center.)
The rocket was the first Delta to use strap-on solid rocket motors, and the spacecraft was the first geostationary satellite. Its predecessor, Syncom-2, had been the first geosynchronous satellite, the difference being that Syncom-2’s orbit was inclined slightly with respect to the equator while Syncom-3’s orbit was more precisely equatorial. The satellite, orbiting over the Pacific, relayed live television coverage of the 1964 Tokyo Olympics.
The Space Science Data Center also notes that
Operations were turned over to the Department of Defense on 1 January 1965, [sic] Syncom 3 was to prove useful in the DoD’s Vietnam communications.
I find this immensely interesting, since from 2001-04 I worked in the Defense Technology Security Administration and enforced restrictions on the export of satellite and launch vehicle technology. Even back in 1964, when I was a “wee bairn,” it was clear that space technology could be dual-use: useful, that is, for civil and military purposes.
Our government seemed to forget that simple fact during the late 1980s and early 1990s, and allowed companies to export space technology a bit more freely; during that time, a few U.S. companies managed to help other countries solve technical problems that enabled them to improve their space technologies. My job at DTSA was to protect those technologies, which not only protected our military advantage but also — though the companies were loathe to admit it — protected the technological edge our U.S. corporations had built up over the years.
Now we seem to be in danger of turning the calendar back and allowing companies to be more laissez faire in exporting militarily critical technologies. The current Administration, under pressure from industry groups that would rather sell technology today even if it means giving up their technological advantage tomorrow, is considering taking satellites off of the U.S. Munitions List. (See this article from July, and this article from last Friday.)
Let me go on record as saying I think this is a bad idea. One, because we don’t need to be giving potential adversaries — or even friendly competitors — the same tools on which we may rely in a conflict. Two, because we don’t need to spare them the years of research and development it will take to catch up — which cost us billions of dollars and included many failures from which we learned valuable lessons — and thereby put them in better positions to compete with us in the future.



 by
by