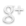Forty-five years ago today — April 3, 1965 — an Atlas Agena-D rocket launched from Vandenberg AFB carrying SNAP-10A, the first nuclear reactor to be launched into space.*

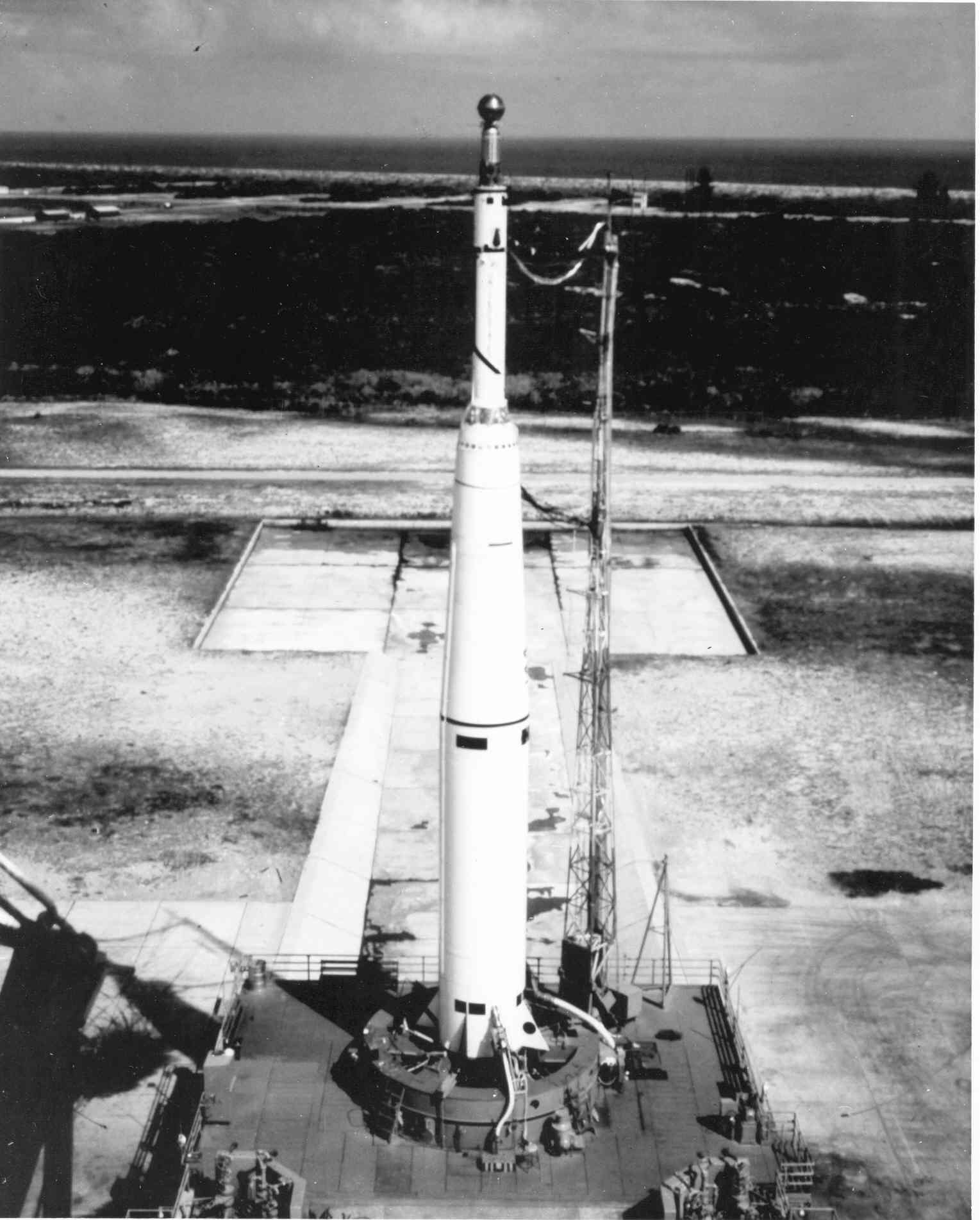
(SNAP-10A reactor undergoing testing. US Department of Energy photo.)
Part of the System for Nuclear Auxiliary Power (SNAP) program, the reactor tested nuclear power generation in the space environment.
The SNAP reactor was designed to be remotely started and operated in space. In this manner, any hazardous radiation associated with the nuclear fission reaction is not produced until after the reactor safely reaches orbit. The hazards to ground personnel are minimized and since radioactive fission products are not present before the reactor is operated, less of a hazard exists during launch if an accidental reentry should occur….
Twelve hours after launch, the nuclear reactor was automatically brought up to operating temperature and initially produced more than 600 watts of electrical power. Following 43 days of successful operation, the reactor was shut down as the result of a high voltage failure in the electrical system of the Agena spacecraft. All flight test objectives were met with the exception of the expected length of operation. The reactor remains in polar orbit today.
Also on this date, 15 years ago, a Pegasus rocket launched from its L-1011 carrier aircraft out of Vandenberg, carrying three small satellites. It launched the lightning mapping satellite MICROLAB-1, along with two ORBCOMM transponders. (To anyone else, that launch is probably not significant, but every Pegasus launch resonates with me because I played a very small role in that program when I was stationed at Edwards AFB.)
___
*Several sources agree that this launch did indeed carry the SNAP-10A reactor; in contrast, the National Space Science Data Center page for this launch states that it carried a SNAP-9A radioisotope thermal generator (the same type to power the Transit series of navigational satellites). Normally the NSSDC pages are quite authoritative, but in this case I believe it has a typo. (As of today, anyway.)



 by
by