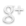Twenty-five years ago today — May 15, 1987 — the USSR launched its first Energia rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome.

(Energia-Polyus, prior to being raised for launch. Image from the Buran-Energia site.)
The Energia was a heavy-lift booster built by the Soviet Union to launch their “Buran” space shuttle. On its maiden flight with the Polyus upper stage instead of Buran, the Energia performed as intended but the upper stage did not place the payload in orbit. According to the Wikipedia entry:
The Soviets had originally announced that the launch as a successful sub-orbital test of the new Energia booster with a dummy payload, but some time later it was revealed that the flight had, in fact, been intended to orbit the Polyus, a UKSS military payload. The two stages of the Energia launcher functioned as designed, but the Polyus payload failed to reach orbit. Due to a software error in its attitude control system, the burn of the Polyus’ orbital insertion motor failed to insert the payload into orbit. Instead, the payload reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific ocean.
According to the Buran-Energia site,
It would seem that Polyus is the Soviet response to the project “Star Wars” launched by the American president Reagan. It was to be in fact a space combat laser station. Finally, we know very few things about this apparatus and its real use. Officially it was intended to make scientific experiments in upper atmosphere.
Very interesting.
[BREAK, BREAK]
Ten years later — on this date in 1997 — the Space Shuttle Atlantis launched from Kennedy Space Center on mission STS-84. The shuttle carried U.S. astronauts Charles J. Precourt, Eileen M. Collins, C. Michael Foale, Carlos I. Noriega, and Edward T. Lu; French astronaut Jean-Francois Clervoy; and Russian cosmonaut Elena V. Kondakova to the Mir space station. Foale stayed on Mir, and the shuttle brought astronaut Jerry Linenger back to Earth after his 123-day space station stay.
Quite a contrast with the cold war days.