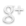Twenty-five years ago today — July 29, 1985 — the Space Shuttle Challenger lifted off from Kennedy Space Center on mission STS-51F. During the launch, the number one main engine shut down ahead of schedule; NASA declared an “Abort To Orbit,” but was able to re-plan the mission to complete all of its objectives.
Astronauts Charles G. Fullerton, Roy D. Bridges, Karl G. Henize, Anthony W. England, F. Story Musgrave, Loren W. Acton and John-David E Bartoe conducted life sciences, plasma physics, astronomy, and other experiments in the Spacelab-2 module before returning to earth on August 6th. They landed at Edwards Air Force Base.

(STS-51F landing at Edwards AFB (August 6, 1985). NASA image.)
(Of personal interest: When we were stationed at Edwards later in the 80s, General Bridges was the AF Flight Test Center commander. We only met him a couple of times, but his son was part of the Protestant Youth of the Chapel group we helped lead.)
Now, for those space history tidbits:
On July 29, 1955 — 55 years ago today — the White House announced the upcoming International Geophysical Year (IGY), for which the U.S. planned to launch a satellite. As you know, the Soviets’ Sputnik beat us to it.
Around this date 50 years ago — one source said July 29, another July 28 — NASA announced that the program aimed at the moon would be named “Apollo.” The name had actually been suggested six months earlier by NASA engineer Abe Silverstein. (Note that this was before President Kennedy was elected, and therefore long before he announced his support of the lunar landing program.)
Finally, on this date 50 years ago — July 29, 1960 — the first unmanned Mercury launch was attempted from Cape Canaveral. Mercury-Atlas-1 (MA-1) exploded at about eight miles altitude. We still had a long way to go.